
Introduction
If you are preparing for a GCP interview, this guide will help you get job-ready. Below, you will find:
- 150+ GCP interview questions
- Scenario-based, real-time, and troubleshooting questions
- GCP Cloud Engineer, DevOps, Architect, Data Engineer questions
- Voice-search-friendly answers
- Featured snippet answers
- GCP vs AWS comparison
- Real-time industry examples
This guide covers everything recruiters in IT companies usually ask during GCP interviews.
What is GCP?
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a cloud computing platform that provides virtual machines, storage, databases, networking, DevOps tools, and AI/ML services hosted on Google’s global infrastructure.
How GCP Works?
GCP works by offering on-demand cloud services like compute, storage, database, networking, security, AI, and DevOps tools that organizations can access via the internet. Users only pay for what they use.
GCP Architecture Overview
GCP architecture is built around:
- Compute (Compute Engine, GKE, Cloud Run)
- Storage (Cloud Storage, Filestore, Persistent Disks)
- Databases (Cloud SQL, BigQuery, Firestore, Spanner)
- Networking (VPC, Load Balancers, Cloud Armor, Cloud CDN)
- IAM & Security
- DevOps (Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy, Cloud Functions)
- Data & ML (BigQuery, Dataflow, Pub/Sub, Vertex AI)
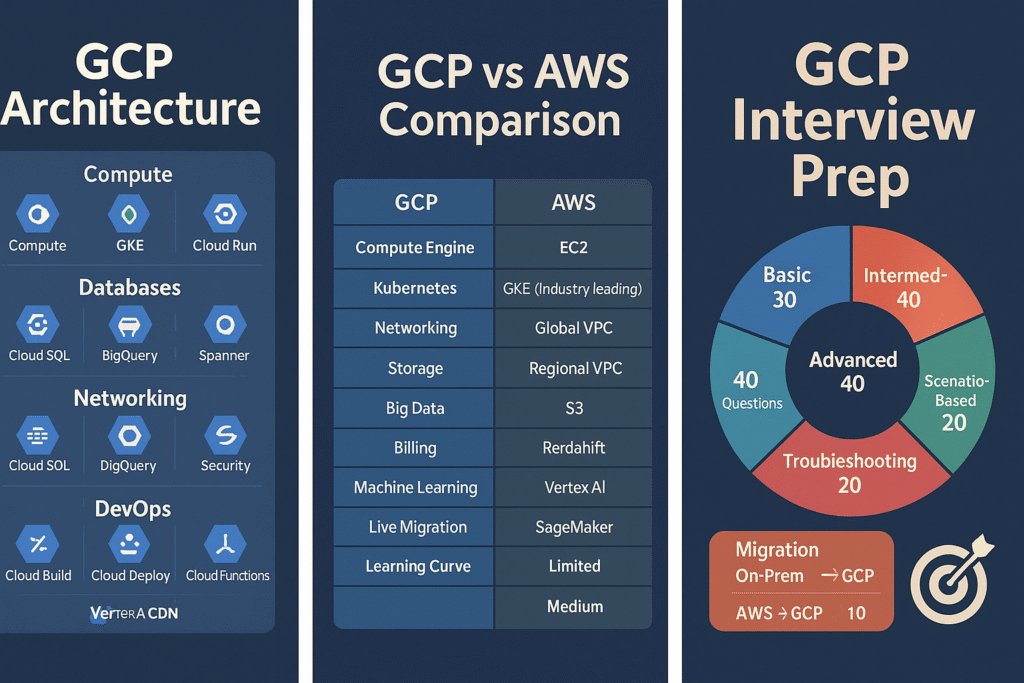
GCP vs AWS Comparison Table
| Feature | GCP | AWS |
|---|---|---|
| Compute | Compute Engine | EC2 |
| Kubernetes | GKE (Industry-leading) | EKS |
| Networking | Global VPC | Regional VPC |
| Storage | Cloud Storage | S3 |
| Big Data | BigQuery | Redshift |
| Billing | Per-second billing | Per-hour/Per-second |
| Machine Learning | Vertex AI | SageMaker |
| Live Migration | Yes | Limited |
| Learning Curve | Easier | Medium |
150+ GCP Interview Questions and Answers
Basic GCP Interview Questions (30)
1. What is GCP?
GCP (Google Cloud Platform) is Google’s cloud service where you can run applications, store data, and use AI, networking, security, and DevOps services.
2. What are the core services in GCP?
The core areas are Compute, Storage, Networking, Databases, Security, and DevOps tools.
3. What is Compute Engine?
Compute Engine is Google’s virtual machine service where you can run Linux or Windows servers.
4. What is GKE?
GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine) is Google’s managed Kubernetes platform for running containerized applications.
5. What is Cloud Run?
Cloud Run is a fully serverless service where you can run containerized apps without managing servers.
6. What is Cloud Functions?
Cloud Functions lets you run small pieces of code triggered by events such as file uploads or Pub/Sub messages.
7. What is BigQuery?
BigQuery is a serverless data warehouse used for fast SQL-based analytics on large datasets.
8. What is Cloud SQL?
Cloud SQL is Google’s managed database service for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
9. What is VPC?
A VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) creates a private network where your GCP resources communicate securely.
10. What is a region in GCP?
A region is a specific geographical area where Google hosts its cloud infrastructure (example: Mumbai, Singapore).
11. What are zones?
Zones are subdivisions inside a region. They provide high availability by distributing workloads across independent data centers.
12. What is IAM?
IAM (Identity and Access Management) controls who can access GCP resources and what actions they can perform.
13. What are Cloud Storage classes?
GCP provides four storage classes based on usage: Standard, Nearline, Coldline, and Archive — each optimized for different access patterns.
14. What is a service account?
A service account is an identity used by applications or VMs to access GCP services securely.
15. What is a billing account?
It’s the account where all cloud charges for your projects are collected and paid.
16. What is a project in GCP?
A project is the main container where you create and organize all your cloud resources, IAM roles, and billing settings.
17. What is a firewall rule?
Firewall rules control incoming and outgoing traffic to your VPC networks using allow or deny rules.
18. What is Cloud Shell?
Cloud Shell is an online terminal provided by Google with pre-installed tools, accessible directly from your browser.
19. What is Cloud Marketplace?
Cloud Marketplace offers ready-to-deploy software like WordPress, Kubernetes apps, databases, and security tools.
20. What is a preemptible VM?
A preemptible VM is a low-cost VM that can be terminated by Google at any time — useful for batch or fault-tolerant workloads.
21. What are labels?
Labels are key-value tags applied to resources for organization, filtering, and cost tracking.
22. What is Cloud CDN?
Cloud CDN speeds up content delivery by caching data at Google’s edge locations worldwide.
23. What is Cloud Armor?
Cloud Armor protects applications from DDoS attacks and allows you to define security rules.
24. What is Cloud Interconnect?
Cloud Interconnect provides high-speed, private connectivity between your data center and Google Cloud.
25. What is Pub/Sub?
Pub/Sub is a messaging service for real-time communication between independent applications.
26. What is Dataflow?
Dataflow is Google’s managed service for running stream and batch data processing pipelines.
27. What is Anthos?
Anthos is a hybrid and multi-cloud platform that helps you run and manage applications across GCP, on-prem, AWS, and Azure.
28. What is Filestore?
Filestore is Google’s managed NFS file storage service, mainly used with applications that require a shared file system.
29. What is Memorystore?
Memorystore is a fully managed Redis or Memcached service used for caching and boosting application performance.
30. What is Vertex AI?
Vertex AI is Google’s unified platform for building, training, deploying, and scaling machine learning models.
Advanced GCP Interview Questions — HUMAN-WRITTEN Answers (40)
ADVANCED GCP INTERVIEW QUESTIONS & ANSWERS (FULL SET — 40)
1. Explain GCP Load Balancing Architecture.
GCP uses global anycast load balancing, where traffic enters the nearest Google edge POP, gets terminated at Google Front Ends, and is routed across Google’s private backbone to healthy backends. It supports L4/L7 load balancing, cross-region failover, CDN integration, autoscaling, and Cloud Armor security.
2. How does BigQuery achieve separation of compute and storage?
Storage lives in Colossus (distributed storage). Compute is handled by Dremel (execution engine) using BigQuery slots. Compute and storage scale and bill independently, enabling serverless performance.
3. What is GKE autoscaling (HPA, VPA, Node Autoscaling)?
- HPA → Scales pods based on metrics like CPU/Memory.
- VPA → Adjusts pod resource requests/limits.
- Node Autoscaler → Adds/removes nodes when pods can’t be scheduled.
4. How does GCP ensure high availability?
Uses multi-zone/multi-region deployments, global load balancing, managed database replicas, durable storage, live migrations for VMs, autoscaling, and SRE-backed SLOs.
5. Multi-region designs in GCP?
Use multi-region Cloud Storage, BigQuery multi-region datasets, Spanner multi-region instances, global LB, replicated backend services, and cross-region failover mechanisms.
6. Explain BeyondCorp security model.
Google’s zero-trust approach: access is based on identity, device posture, and context, not network location. Implemented via Identity-Aware Proxy, context-aware access, and Cloud Identity.
7. How does IAM policy inheritance work?
Permissions flow from: Organization → Folder → Project → Resource. Children inherit parent roles unless restricted by deny policies.
8. Difference between Audit Logs types?
- Admin Activity Logs – track resource changes (always on).
- Data Access Logs – track reading/writing data.
- System Event Logs – track system-managed operations.
- Policy Denied Logs – record denied access attempts.
9. How does Cloud Armor rate limiting work?
Creates rules that limit traffic based on IP, geographic location, or custom attributes. Protects against DoS attacks by throttling requests exceeding thresholds.
10. When to choose Cloud Run vs GKE?
- Cloud Run → Serverless, fast deployment, stateless workloads.
- GKE → Microservices, complex workloads, custom networking, sidecars.
11. How does BigQuery BI Engine work?
In-memory analytics engine that accelerates dashboards by caching and pre-computing results, offering sub-second queries.
12. Explain Private Service Connect.
Allows private access to Google APIs or third-party services using internal IPs, avoiding public internet exposure.
13. Steps for hybrid connectivity design?
- Choose connectivity (VPN/Interconnect)
- Configure Cloud Router
- Establish BGP sessions
- Set up routing tables
- Configure firewall rules
- Validate failover and redundancy
14. How does the GCS consistency model work?
GCS is strongly consistent for read-after-write, object listing, and metadata updates.
15. Difference between CMEK and CSEK?
- CMEK → Keys stored in Cloud KMS.
- CSEK → Customer-provided raw encryption keys supplied to Google.
16. How to optimize GKE costs?
Use autoscaling, preemptible nodes, resource right-sizing, workload separation via node pools, and GKE autopilot mode.
17. Explain IAM role types.
- Basic roles → Viewer, Editor, Owner.
- Predefined roles → Service-specific minimal roles.
- Custom roles → Fine-grained permissions chosen by user.
18. How to secure service accounts?
Avoid keys, use Workload Identity, restrict permissions, limit impersonation, monitor audit logs.
19. Explain VPC Service Controls.
Creates security perimeters around services like BigQuery/GCS to prevent data exfiltration.
20. What is a GKE node pool?
A group of nodes with the same configuration (machine type, OS). Used to optimize workloads by separating compute types.
21. Multi-tenancy designs in GCP?
Use separate projects per tenant, Shared VPC, IAM boundaries, dataset-level access control, and VPC SC for sensitive data.
22. How does Workload Identity work?
Maps Kubernetes service accounts to Google service accounts, eliminating the need for service account keys.
23. Explain Dataflow autoscaling.
Adjusts worker nodes dynamically based on backlog, throughput, and CPU usage for both batch and streaming jobs.
24. BigQuery materialized views use case?
Used for precomputed results of heavy queries, improving dashboard performance and reducing storage costs.
25. Cloud Spanner TrueTime explained.
A globally synchronized clock using GPS + atomic clocks with bounded uncertainty, enabling strong consistency globally.
26. How does Google’s internal network improve performance?
Uses private fiber optics, edge POPs, global routing, and congestion control to ensure low latency and high throughput.
27. Multi-cluster GKE design?
Use regional clusters, multiple clusters per environment, multi-cluster ingress, federation, and service mesh for traffic routing.
28. Anthos Service Mesh explained.
Provides mTLS, policy enforcement, traffic management, and observability across hybrid/multi-cloud Kubernetes clusters.
29. PKI integration in GCP?
Use Certificate Authority Service (CAS) to issue certificates for internal services, integrated with LBs, GKE, and ASM.
30. How Pub/Sub exactly-once works?
Uses message IDs, consumer deduplication logic, and BigQuery/Dataflow transactional sinks to guarantee effective exactly-once behavior.
31. What are BigQuery federated queries?
Queries external data sources like GCS, Cloud SQL, Sheets, Bigtable, without loading data into BigQuery.
32. IAM least privilege best practices?
Use predefined roles, deny policies, service account scoping, Workload Identity, periodic audit log reviews.
33. How to secure Cloud Run services?
Enforce IAM auth, restrict ingress, use VPC connectors, set minimum instances, and restrict egress with Cloud NAT.
34. Key rotation strategies in KMS?
Enable automatic rotation, use versioned keys, periodically re-encrypt sensitive data, monitor audit logs.
35. When to choose Filestore vs Persistent Disk?
- Filestore → Shared file system (NFS).
- PD → Block storage for a single VM; higher IOPS.
36. CI/CD with Cloud Build + GitHub?
Use Cloud Build triggers on push/PR, build images, store in Artifact Registry, deploy to Cloud Run/GKE using pipelines.
37. GCP network segmentation strategies?
Use Shared VPC, firewall policies, separate projects, VPC SC, private service access, and strict IAM boundaries.
38. Dataflow vs Dataproc comparison?
- Dataflow → Serverless Beam pipelines (ETL/streaming).
- Dataproc → Managed Hadoop/Spark clusters for lift-and-shift.
39. Multi-cloud deployment using Anthos?
Run GKE anywhere (AWS/Azure/on-prem), unify policy, use Anthos Service Mesh, and centrally manage services.
40. BigQuery slot management strategies?
Use reservations, assignments per workload, autoscale, optimize SQL patterns, and use Flex Slots for short-term needs.
SCENARIO-BASED GCP INTERVIEW ANSWERS (20) — FULL DETAILED ANSWERS
1. Spike in traffic — what do you do?
Enable autoscaling on Compute Engine/GKE, use Cloud CDN for caching static content, configure global load balancer with cross-region failover, optimize backend capacity.
2. VM needs private internet access — solution?
Use Cloud NAT to enable outbound internet access while keeping VM private (no external IP).
3. Need real-time streaming analytics — what to use?
Use pipeline: Pub/Sub → Dataflow (streaming) → BigQuery for near real-time analytics.
4. App must run serverless — which service?
Use Cloud Run for containerized serverless workloads (or Cloud Functions if event-driven lightweight code).
5. Need to secure internal enterprise applications — how?
Use Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP) + Private Service Connect to allow only authenticated users on private networks.
6. Migrate 1 TB data warehouse — best option?
Use BigQuery Data Transfer Service or Storage Transfer Service depending on source.
7. Batch processing workflow — recommended solution?
Use Cloud Storage upload triggers → Cloud Functions → downstream processing.
8. Need multi-cloud Kubernetes cluster — how?
Use Anthos GKE to manage and standardize clusters across AWS/Azure/on-prem/GCP.
9. Sub-second analytics for dashboards — solution?
Use BigQuery BI Engine for in-memory acceleration and low-latency dashboard queries.
10. Low-latency ML inference — best GCP service?
Use Vertex AI Endpoints with GPU/TPU-backed VMs for high-performance inference.
11. Need automated ETL pipelines — service to use?
Use Cloud Composer (Apache Airflow) for complex workflow orchestration.
12. Deploy container from GitHub — easiest method?
Use Cloud Build triggers connected to your GitHub repository.
13. Global application deployment — what’s required?
Use Global HTTP(S) Load Balancer, multi-region backends, multi-region storage, and failover policies.
14. Need API throttling and rate limiting — which GCP service?
Use Apigee API Management with its quota, spike arrest, and rate-limiting policies.
15. Quick user authentication — best service?
Use Firebase Authentication (email, phone, OAuth, SSO).
16. Distributed SQL database with high availability — GCP solution?
Use Cloud Spanner, providing global consistency and horizontal scaling.
17. Event-driven microservices — architecture?
Use Pub/Sub for messaging + Cloud Run/Functions for event processing.
18. Data lake design — how to build?
Use GCS for raw zone, Dataflow for transformation, and BigQuery for analytics.
19. Need strong data security boundary — what to use?
Use VPC Service Controls to prevent data exfiltration from sensitive services.
20. Need to stream logs to SIEM — solution?
Use Log Sinks → Pub/Sub → SIEM (like Splunk, Chronicle).
GCP TROUBLESHOOTING ANSWERS (20) — FULL DETAILED ANSWERS
1. VM unreachable — what to check?
Check firewall rules, network tags, VPC routes, and external/internal IPs.
2. GKE pod pending — why?
Node pool may have insufficient resources or taints; scale nodes or adjust tolerations.
3. BigQuery query slow — fix?
Add partitioning, clustering, reduce unneeded columns, optimize SQL logic.
4. Cloud Run returning 403 — why?
Missing IAM role Cloud Run Invoker. Add permission to caller or service account.
5. VM bill suddenly high — reason?
Idle/redundant VMs, disks, snapshots, or egress. Use Billing Recommender.
6. Load Balancer 502 errors — what causes it?
Unhealthy backends or incorrect health check path/ports.
7. GCS upload failing — reason?
Bucket IAM issue; missing storage.objectCreator or VPC SC restrictions.
8. Pub/Sub message lag — fix?
Increase subscribers, use parallel pull, tune ack deadlines.
9. Dataflow job stuck — what to check?
Worker errors, quota issues, hot keys; increase max workers.
10. SQL connection timeout — common causes?
Connection limits, missing indexes, high latency, or private IP routes.
11. Cloud Build failure — reason?
Wrong cloudbuild.yaml config or missing IAM permissions.
12. Composer DAG not running — why?
Scheduler down, task dependencies unsatisfied, or DAG disabled.
13. Network intermittent drops — what causes it?
Overlapping CIDR ranges, routing conflicts, misconfigured VPC Peering.
14. PSC failing — reason?
DNS not resolving to PSC endpoint or firewall blocking internal traffic.
15. Cloud Armor blocking valid traffic — why?
Rule priority incorrect; whitelist missing; policy order problem.
16. Spanner high latency — fix?
Create secondary indexes, reduce cross-region writes, or use stale reads.
17. Cold starts in Cloud Run — solution?
Set minimum instances to keep containers warm.
18. BigQuery “unauthorized” error — why?
Wrong service account used or missing dataset-level IAM.
19. NAT not working — what causes it?
Routing priorities incorrect or subnet not attached to NAT gateway.
20. GKE ingress not working — why?
Ingress controller not deployed properly, wrong annotations, or unhealthy backend service.
GCP MIGRATION ANSWERS (10) — FULL DETAILED ANSWERS
1. Lift-and-shift from On-Prem → GCP
Use Migrate to VMs (formerly Velostrata). Supports replication, test migrations, and controlled cutover.
2. Database migration — which tool?
Use Database Migration Service (DMS) for MySQL/PostgreSQL/SQL Server with minimal downtime.
3. AWS S3 → GCS migration — how?
Use Storage Transfer Service or gsutil -m rsync for bucket-to-bucket transfer.
4. On-prem Hadoop → GCP migration?
Use Dataproc migration (HDFS → GCS, Hive/Spark → Dataproc).
5. AWS Redshift → BigQuery — process?
Export to S3 → Transfer to GCS → Dataflow for schema mapping → Load to BigQuery.
6. VM migration with minimal downtime — GCP service?
Use Migrate to VMs continuous replication + cutover window.
7. MySQL migration → Cloud SQL — how?
Use Cloud SQL DMS, supports CDC-based replication and seamless cutover.
8. Large dataset migration (10–100 TB+) — solution?
Use Transfer Appliance, shipped to your data center.
9. Kubernetes migration — how?
Use Anthos GKE, migrate workloads via Helm/YAML; standardize mesh and security.
10. Hybrid network migration — steps?
Start with IPSec VPN, later upgrade to Interconnect for high throughput; configure BGP and routing.
Real-Time Use Cases of GCP
- E-commerce scaling (Flipkart-like workloads)
- Banking analytics using BigQuery
- Startups using Cloud Run for serverless apps
- ML models deployed using Vertex AI
- Media streaming platforms using GCS + CDN
Industry Scenarios (Hyderabad, Bangalore, Pune, Chennai)
- Hyderabad: Heavy GCP usage in BFSI & pharma analytics
- Bangalore: Startups & product companies prefer GCP for ML workloads
- Pune: IT service companies use GCP for migration projects
- Chennai: Manufacturing & automotive firms use GCP IoT & data analytics
Conclusion
This guide covers 150+ GCP interview questions, including basics, advanced topics, real-time scenarios, troubleshooting, and migration.
If you’re preparing for a cloud job in India, this list will help you clear interviews confidently.
FAQs
- Is GCP good for freshers?
Yes, especially for Cloud Engineer and DevOps roles. - Is GCP easier than AWS?
Many find GCP easier. - Which certification to start?
Associate Cloud Engineer. - How long to prepare?
2–4 weeks basics, 2 months advanced. - Is GCP in demand in India?
Very high in Hyderabad, Bangalore, Pune. - Best area of specialization?
GCP DevOps, GCP Data Engineering. - Which GCP job has highest salary?
Cloud Architect / Data Engineer. - Do Indian companies use GCP?
Yes—TCS, Wipro, Infosys, Tech Mahindra, Accenture. - Is GCP good for Kubernetes?
Yes—GKE is industry-leading. - Is BigQuery better than Redshift?
For serverless analytics, yes.
